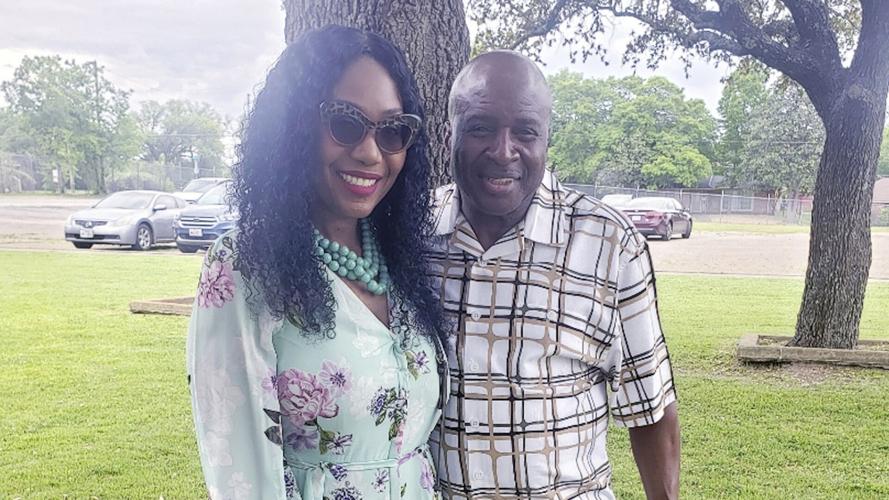
PHOENIX — Postal worker Eugene Gates Jr. was delivering mail in the suffocating Dallas heat this summer when he collapsed in a homeowner's yard and was taken to a hospital, where he died.
Carla Gates said she's sure heat was a factor in her 66-year-old husband's death, even though she's still waiting for the autopsy report. When Eugene Gates died on June 20, the temperature was 98 degrees Fahrenheit (36.6 Celsius) and the heat index, which also considers humidity, had soared over 110 degrees Fahrenheit (43.3 Celsius).
“I will believe this until the day I die, that it was heat-related," Carla Gates said.

This undated photo provided by Carla Gates shows Gates and her husband, Dallas mail carrier Eugene Gates Jr. On June 20, 2023, Eugene Gates collapsed on a homeowner’s property when he was making deliveries on a suffocating hot day and later died at a hospital.
Even when it seems obvious that extreme heat was a factor, death certificates don't always reflect the role it played. Experts say a mishmash of ways more than 3,000 counties calculate heat deaths means we don't really know how many people die in the U.S. each year because of high temperatures in an ever warming world.
People are also reading…
That imprecision harms efforts to better protect people from extreme heat because officials who set policies and fund programs can't get the financial and other support needed to make a difference.
“Essentially, all heat related deaths are preventable. People don’t need to die from the heat," said epidemiologist Kristie L. Ebi, who focuses on global warming’s impact on human health as a professor at the University of Washington.
With a better count, she said, “you can start developing much better heat wave early warning systems and target people who are at higher risk and make sure that they’re aware of these risks.”
Currently, about the only consistency in counting heat deaths in the U.S. is that officials and climate specialists acknowledge fatalities are grossly undercounted.
"Deaths are investigated in vastly different ways based on where a person died,” said Dr. Greg Hess, the medical examiner for Pima County, Arizona's second most populous county and home to Tucson. “It should be no surprise that we don't have good nationwide data on heat-related deaths.”
Many experts say a standard decades-old method known as counting excess deaths could better show how extreme heat harms people.
“You want to look at the number of people who would not have died during that time period and get a true sense of the magnitude of the impact,” Ebi said, including people who would not have suffered a fatal heart attack or renal failure without the heat.

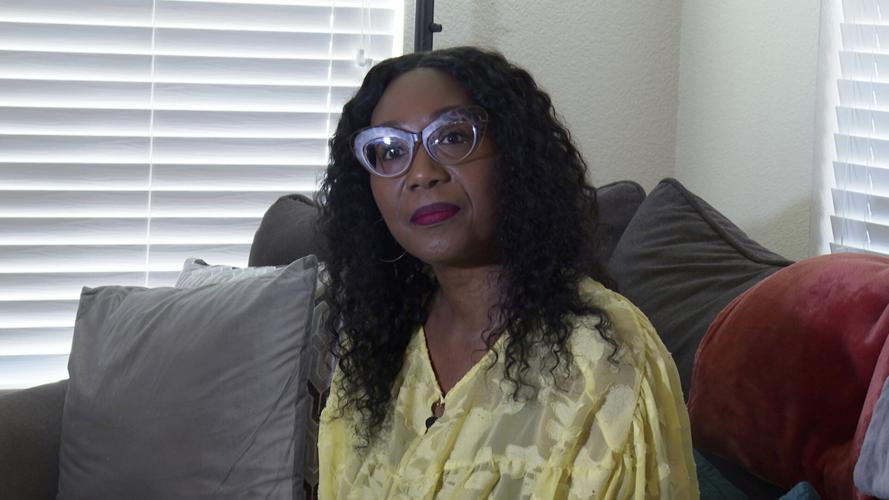
In this screen grab from video, Carla Gates is seen during an interview in Dallas, Tuesday, Aug. 8, 2023. Gates' husband, a postal carrier, was delivering mail in the suffocating Dallas heat this summer when he collapsed in a homeowner's yard and was taken to a hospital, where he died.
The excess deaths calculation is often used to estimate the death toll in natural disasters, with researchers tallying fatalities that exceeded those that occurred at the same time the previous year when circumstances were average.
Counting excess deaths was used to calculate the human impact of a heat wave in Chicago that killed more than 700 people in July 1995, many elderly Black people who lived alone. Researchers also counted excess deaths during the COVID-19 pandemic to provide more complete information about deaths directly and indirectly related to the coronavirus.
But as things stand now, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports just 600 to 700 heat deaths annually in the United States. A study published last month in the journal Nature Medicine estimated more than 61,000 heat-related deaths last summer across Europe, which has roughly double the U.S. population but more than 100 times as many heat deaths.
Dr. Sameed Khatana, a staff cardiologist at the Philadelphia VA Medical Center and assistant professor at the University of Pennsylvania’s Perelman School of Medicine, has said deaths in which heat contributed significantly to fatalities from causes like heart failure should also be considered.
Khatana participated in research published last year that counted excess deaths in all U.S. counties. The findings suggested that from 2008 to 2017 between 3,000 to 20,000 adult deaths from all causes listed on death certificates were linked to extreme heat. Heart disease was listed as the cause of about half of the deaths.
After the Pacific Northwest heat wave in summer of 2021, the Canadian province of British Columbia reported more than 600 deaths due to heat exposure while Oregon and Washington each initially reported a little more than 100 such fatalities.
“It’s frustrating that for 90 years public health officials in the United States have not had a good picture of heat-related mortality because we have such a bad data system,” said Dr. David Jones, a Harvard Medical School professor who also teaches in the epidemiology department at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
There is no uniformity among who does the counting across U.S. jurisdictions. Death investigations in some places might be carried out by a medical examiner, typically a physician trained in forensic pathology. In other locales, the coroner could be an elected sheriff, such as the one in Orange County, California. In some small counties in Texas, a justice of peace might determine cause of death.
Utah and Massachusetts are among states that do not track heat-related deaths where exposure to extreme heat was a secondary factor.
The CDC, which is often several years behind in reporting, draws information on heat deaths from death certificate information included in local, state, tribal and territorial databases.
The CDC said in a statement that coroners and others who fill out death certificates “are encouraged to report all causes of death,” but they may not always associate those contributing causes to an extreme heat exposure death and include the diagnostic codes for heat illnesses.

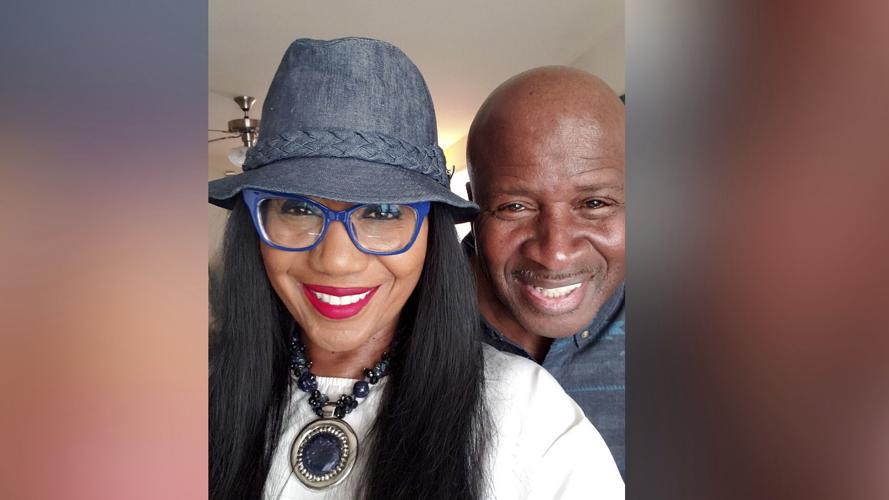
This undated photo provided by Carla Gates shows Gates and her husband, Dallas mail carrier Eugene Gates Jr. On June 20, 2023, Eugene Gates collapsed on a homeowner’s property when he was making deliveries on a suffocating hot day and later died at a hospital.
Hess, the Arizona coroner, said determining environmental heat was a factor in someone's death is difficult and can take weeks or even months of investigation including toxicological tests.
“If someone was shot in the head, it's pretty obvious what happened there," Hess said. “But when you find a body in a hot apartment 48 hours after they died, there is a lot of ambiguity.”
Hess noted that Pima County this year began including heat-related deaths in its tally of environmental heat fatalities. Maricopa County, home to Phoenix, America's hottest big city, for years has included heat-related deaths. Clark County, Nevada, home to Las Vegas, now also considers deaths in which heat was a contributing factor.
Maricopa's Public Health Department counted 425 “heat associated” deaths last year, including those where heat was a secondary factor, such as a heart attack provoked by high temperatures.
It reports there were 59 heat-associated deaths confirmed this year through Aug. 5, with another 345 under investigation. The latest count follows the hottest month in Phoenix on record, and a record 31 consecutive days that hit 110 degrees Fahrenheit (43.3 Celsius) or higher.
Dallas, which regularly sees summer highs over 100 degrees Fahrenheit (37.7 Celsius), sweltered through an excessive heat warning this month and also grapples with oppressive humidity.
Carla Gates, whose mail carrier husband died, noted cities worldwide now must learn to deal with extreme weather. She said her spouse, with 36 years on the job, tried to protect himself by taking a chest filled with ice and several bottles of cold water on his rounds.
“Our climate has changed,” she said. “And I don’t think it’s going back to how it was 20 years ago. So we’re going to have to get used to it and we’re going to have to make some adjustments.”
Now she wants to honor her husband by pushing legislation to ensure people working outside are better protected from the heat. Gates noted that the day her husband died he was in an old mail truck without working air conditioning.
“I don’t wish this on anyone, anyone to get a phone call that their loved one died working, doing something that they love in the heat,” she said.
___
LaFleur reported form Dallas. AP writers from around the U.S. also contributed.
How climate change drives hotter, more frequent heat waves
How climate change drives hotter, more frequent heat waves

In late June 2021, a high-pressure atmospheric system settled over Seattle to create an inescapable heat dome. Jean-Paul Yafali, a resident of nearby Kent, Washington, thanked his good luck for the two secondhand air-conditioning units that a friend had given him back in 2019. He wasn't used to this kind of stifling heat — not in Seattle, and not even in Kinshasa, Congo, where he grew up.
"I'm from a country where it's really hot," Yafali told Grist. But during Seattle's heat dome, "it was impossible for me to last a couple minutes" outside.
By Monday the 28th, the temperature in Seattle would climb to a record-breaking 108 degrees Fahrenheit, nearly 40 degrees above normal for that time of year. National Weather Service officials warned that the pavement could reach 170 degrees in some places. Yafali and his family found respite in their AC, but they were fortunate outliers; Seattle, known for its cool, wet winters and mild summers, is one of the least air-conditioned big cities in the country. To avoid overheating, people boarded up windows with cardboard boxes. They soaked their feet in buckets of cold water and bought squirt bottles. They took refuge in shady parks or in community cooling centers.
The Pacific Northwest heat wave of 2021 was one of the most extreme ever recorded globally, a "historic, dangerous, prolonged, and unprecedented" event that took a hefty toll on people and infrastructure. Between British Columbia, Washington state, and Oregon, more than 800 people died and thousands more visited the emergency room for heat-related conditions like kidney failure and encephalopathy. Police officials in Vancouver said they spent entire 12-hour shifts going "from one sudden death to another."

Is climate change to blame?

The blistering weather had many people wondering: Is this climate change?
The short answer is yes. Grist reporting has found that although the event was exceedingly abnormal — a 1-in-1,000-year event in today's climate, according to some estimates — researchers say that without global warming it would have been at least 150 times rarer and several degrees cooler.
Indeed, heat waves around the world are happening more frequently and reaching higher temperatures because of climate change. We know this thanks to the rapidly growing field of attribution science, which allows scientists to examine the link between rising levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide and extreme weather events. When a heat wave strikes — or another disaster, for that matter, be it a hurricane, drought, or very heavy rain — attribution scientists can determine the role that climate change played in its intensification.
With extreme heat in particular, the answer is often tens or even hundreds of times more likely, thanks to a complicated mix of factors like abnormally dry soils and hotter-than-usual air. In fact, scientists are now comfortable assuming that all heat waves are being made more severe or likely because of climate change.
At any given time, extreme heat is now affecting about one-tenth of the Earth's land area, and scientists have observed an eightfold increase in record-breaking hot months over the past decade, compared to what would be expected in a world without climate change. Already, the U.S. is experiencing periods of abnormally hot weather at least three times more often than it did in the 1960s. Researchers estimate that another 1 degree Celsius (1.8 degrees F) of warming could turn something like the Pacific Northwest's freak heat dome into a once-in-a-decade affair.
A cooling weather pattern called La Niña has suppressed global temperatures since 2020, but scientists announced this spring that a new, hotter pattern — El Niño — is emerging to replace it. Although experts say its full effects won't be felt until next summer, it may already be contributing to some of this summer's heat extremes.
In early July, Earth logged its seven hottest days ever. And in June, a punishing heat dome brought triple-digit temperatures to more than 55 million people across the Southern U.S., straining emergency services and causing more than a dozen deaths. The heat was exacerbated in states like Louisiana, where high humidity combined with searing temperatures to create a heat index of up to 125 degrees F, meaning what the body feels, not just what the thermometer says.
Heat, one of the best-understood extreme weather events tied to climate change, doesn't tend to draw the same attention as other disasters like hurricanes and wildfires. But that may be starting to change. In the U.S., scorching temperatures cause more deaths than any other weather-related disaster, claiming nearly 170 lives every year. And as climate change drives global temperatures even higher, heat waves will only become more lethal, disrupting the lives of billions of people across the planet.
Understanding heat waves

Unlike other extreme weather events, heat waves are highly context-dependent. That is, they're defined by their deviation from what's considered a normal temperature for a given place. When the mercury hits 95 degrees F in San Francisco, for example, that might be considered a heat wave — but not so in Phoenix, where summertime temperatures routinely exceed 100 degrees F.
Most heat waves do share a common origin story, though. Broadly speaking, they form when a high-pressure air system parks itself over land, forcing air to sink to the ground. This air heats up as it compresses and becomes trapped, unable to dissipate into the upper atmosphere. Such a system also makes cloud formation less likely. (Cold air forces water out relatively quickly compared to hot air, and this water becomes clouds.) This allows more sunlight to reach the ground and exacerbate warming.
Radley Horton, a scientist who studies ocean and climate physics at Columbia University, said there are a few additional "ingredients" that can converge to create a heat wave. Drier conditions, for example, mean more of the sun's energy can go toward heating the air rather than evaporating water from plants and the soil. The time of year can also play a role: At latitudes farther from the equator, the Earth's tilt can lead to summer days with 15 hours or more of sunlight — a long time for heat to build up.
All these factors in combination are "a recipe for a lot of sunlight and warming, stagnant air," Horton said.
Huge atmospheric wind patterns called jet streams also play a role in forming heat waves. These jet streams — like the subtropical jet stream that affects the U.S. — are driven by temperature gradients between the warm tropics and the colder poles. They carry air from west to east across the globe, but also wobble from north to south. When the subtropical jet stream bulges north, it can invite warm air from the south and trap it in place, leading to what scientists call atmospheric blocking.
"When the jet stream meanders, it creates a heat dome, a pool of very warm air under this displaced jet stream," said Noboru Nakamura, an expert on atmospheric and environmental fluid dynamics at the University of Chicago. "It's almost like a warm blanket."
This is what happened to an extreme degree in the Pacific Northwest in June 2021. A particularly strong blocking pattern called an omega block — so named for its resemblance to the Greek letter of the alphabet — anchored itself above Oregon, Washington, and British Columbia for several days, combining with other favorable factors like dry air and proximity to the summer solstice, the longest day of the year. The result: "unheard of" surface temperatures, as Nakamura put it, that reached as high as 121 degrees F in Canada. A similar phenomenon was behind last month's heat dome in the South, where temperatures climbed to 119 degrees F in parts of Texas.
Analyzing the likelihood of a heat wave under climate change

In a way, it seems intuitive that extreme heat would be getting worse in the face of climate change. Global warming, after all, involves warming. But scientists have a way to more rigorously test that intuition: They use computer models to reconstruct the global climate with and without human-added greenhouse gas emissions, and then compare the likelihood of a heat wave in either scenario.
There are a few ways to go about these analyses. The most common, known as probabilistic analysis, is used to produce statistics about a heat wave's increased likelihood and intensity under climate change. First, scientists identify an extreme heat event and chart it against other observed extremes going back 50 or more years (the longer the better, depending on the data available). Then they use climate models to simulate how anomalous the event would be in today's climate versus the climate of the preindustrial 1800s, before global warming.
Consider the "1-in-400-years" heat wave that hit Spain, Portugal, Morocco, and Algeria this April. Over the course of a few days, "superheated air" from the Sahara Desert swept through the region, bringing temperatures that were up to 36 degrees F above normal for that time of year. At the Córdoba airport in Spain, the thermometer hit 102 degrees F — the hottest April temperature ever recorded in Europe. Researchers at World Weather Attribution, an international collaboration among climate scientists, plotted the region's highest expected three-day temperatures in today's climate against the expected time interval between those temperature extremes. (The higher the temperature, the less frequently you'd expect it to occur.) When they compared this to simulations of a world with 1.2 degrees C (2.2 degrees F) less warming, they found that a heat wave like April's is now likely to occur every 100 years, rather than every 400, and is about 3.5 degrees C (6.3 degrees F) hotter.
Scientists have reached similar conclusions for dozens of other heat waves. Out of more than 150 heat-related attribution studies that researchers have conducted since the early 2000s, more than 93 percent have shown evidence of human influence. "You can be confident that heat waves are increasing everywhere globally due to climate change," said Sarah Kew, a climate researcher at the Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute and a core contributor to World Weather Attribution, an academic collaborative.
According to the United Nations' Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, heat waves that used to happen once every decade in the preindustrial era are now happening nearly three times as often and are 1.2 degrees C (2.2 degrees F) hotter. At 2 degrees C (3.6 degrees F) of warming — the upper limit that nearly 200 countries have agreed to as part of the Paris Agreement — they'll happen 5.6 times per decade and will be 2.6 degrees C (4.7 degrees F) hotter.
Although rapid weather attribution studies don't usually consider the specific reasons why climate change is making heat waves worse, Horton, the Columbia University professor, said there are a few heat wave ingredients that can be reliably linked to climate change: drying soils and vegetation, for example, or warming bodies of water that can't cool the air as much as they used to. Some experts also suspect that the warming Arctic — which has heated up four times faster than the rest of the planet since 1979 — could be causing a slower, wobblier jet stream, which would be more conducive to atmospheric blocking. But this is still an area of debate.
Other researchers are also beginning to show how heat waves can have knock-on effects for other natural disasters. Marine heat waves, for example — which have become more common over the past decade — may contribute to stronger hurricanes, since they warm up air above the water. This extra heat lowers the pressure and can create swirling, hurricane-force winds. High heat is also a key ingredient in tornadoes and severe thunderstorms that cause lethal flooding, making it possible that these disasters will get worse with more frequent and intense heat waves.
Droughts and wildfires also interact with heat waves in sometimes complicated ways: A heat wave can often exacerbate drought, drying out soils and plants by increasing "evaporative demand," a measure of how thirsty the atmosphere is. This in turn can create conditions that are ripe for wildfire, as forests and grasslands dry out. But, as noted above, these parched conditions can also make heat waves more powerful — creating a feedback loop in which dry conditions and scorching temperatures reinforce each other. Researchers estimate that, under 2 degrees C (3.6 degrees F) of warming, compound events where both heat waves and drought occur simultaneously will become more severe and happen about once every eight years — four times more often than in the mid-20th century.
Protecting at-risk populations from heat waves

As heat waves worsen, so too does the sense of dread they bring to vulnerable populations.
"Even before it happens, there's a lot of anxiety," said Esther Min, director of environmental health research partnerships for the nonprofit Front and Centered, a coalition of Washington state-based organizations led by communities of color. "It's already brutal on the physical body when it is hot, but if you know it's going to be difficult and you might not be able to escape it? … There's that mental health aspect that I hear people these days talking about a lot more — that anxiety, that grief, that frustration."
This only compounds the physical risks of heat waves, she added, which may include everything from dehydration to heat stroke. As with virtually every other climate impact, these risks are inequitably distributed. They fall disproportionately on poor people, many of whom can't afford an AC unit or the added electricity costs that come with it, or on people of color, who may live in redlined neighborhoods that experience an urban heat island effect thanks to a lack of cooling tree cover and green space. Such areas can feel up to 20 degrees hotter than other neighborhoods — usually whiter, more affluent ones with more greenery.
Children, the elderly, and people experiencing homelessness are also ill-protected from extreme heat. "We need to think of how we can protect these vulnerable populations," said Yafali, who works for the organization Nested Communities to provide rental assistance, transportation services, and other aid to Seattle-area youth of color who are at risk of losing their housing. He said many of the people he works with have struggled to cope with the region's increasingly frequent bouts of extreme heat.
As the heat gets worse, community organizers like Yafali and other groups across the country are calling for a range of solutions, including more heat pumps in apartment buildings — which provide both heating and cooling — and community monitoring systems to check in on at-risk neighbors. Seattle is looking at some of these solutions as part of its first-ever extreme heat mitigation strategy. Martha Lucas, executive director of the Washington State Coalition of African Community Leaders, said something as simple as better communication systems could also help. A lot of the people she works with don't use email or don't speak English, she said, making it harder for them to receive temperature warnings and guidance on how to keep cool. "They have a wide range of ages and abilities, and not everybody understands," she said.
Still, progress is slow and some people are already being pushed to their limits. Even with his AC units, Yafali is nervous for Seattle's next heat wave — especially how it will affect his young daughters. Back in 2021, he saw them through the extreme heat by checking in compulsively, making sure they were drinking enough water and not spending more than 30 minutes at a time in the blazing sun. "We were able to navigate the heat dome," he said, even as he witnessed many others deal with crippling heat cramps and exhaustion.
"I'm really worried," he said. "We have to better prepare."
This story was produced by Grist and reviewed and distributed by Stacker Media.